Confused about choosing hydroxyapatite vs fluoride for better dental health? Many worry about tooth sensitivity, dental fluorosis, or how best to strengthen tooth enamel.
While fluoride toothpaste—often containing sodium fluoride—has long been a go-to for fighting tooth decay, growing interest in hydroxyapatite toothpaste is reshaping the conversation around oral health and dental caries. Understanding how each protects tooth enamel and supports tooth structure is key.
In this guide, we break down the differences and benefits so you can make the best choice for your smile.
Key Takeaways
-
Hydroxyapatite and fluoride are complementary compounds used in dental care, each with unique mechanisms for enamel remineralization and cavity prevention.
-
Hydroxyapatite is biocompatible and non-toxic, making it a safer alternative for all age groups, while fluoride is effective but poses risks of toxicity if overused.
-
Both compounds have demonstrated clinical efficacy in preventing dental caries, with emerging research indicating that their sequential use may enhance protective effects on teeth.
Understanding Hydroxyapatite and Fluoride
If you're weighing the pros and cons of hydroxyapatite vs fluoride, you're not alone. These two natural minerals have become mainstays in dental care, each offering distinct advantages for maintaining oral health and protecting tooth enamel.
To make an informed choice for your oral hygiene routine, it’s worth understanding how each ingredient works—and what makes one better suited for your needs than the other.
What Is Hydroxyapatite?
Hydroxyapatite makes up 97% of tooth enamel and 70% of bone—truly a cornerstone of your body’s natural structure. It’s also at the forefront of modern oral care thanks to its ability to repair enamel, reduce tooth sensitivity, and restore demineralized enamel without the risks associated with overexposure to fluoride.
Today’s hydroxyapatite-based toothpaste often includes nano-hydroxyapatite particles or hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, which are small enough to fill microscopic surface irregularities, enhance enamel repair, and support enamel strengthening. These particles actively bind to the surface of the teeth, releasing phosphate ions and calcium to initiate the remineralization process—helping to remineralize teeth and reduce tooth sensitivity.
Because hydroxyapatite is biocompatible and safe if swallowed, it’s often recommended by dental professionals for children, those with sensitive teeth, and individuals seeking a natural alternative to traditional fluoride-based dental products. And unlike some other treatments, it works harmoniously with your body to rebuild enamel on a molecular level.
For patients seeking a science-backed, gentle solution, nano hydroxyapatite toothpaste offers an exciting advancement that fits easily into a modern oral hygiene routine.
What Is Fluoride?
Fluoride, also a natural mineral, has long been trusted in dentistry for its ability to prevent tooth decay and cavities. It’s commonly found in fluoride toothpaste, drinking water, and many toothpaste formulations approved by health authorities worldwide.
You’ll often see fluoride in three forms: sodium fluoride, stannous fluoride, and monofluorophosphate—each with distinct benefits. In toothpaste, these compounds interact with the minerals in your enamel to form fluorapatite, a harder, more acid-resistant substance that defends against acid attacks from plaque and sugary foods. This helps to strengthen tooth enamel and improve overall oral health.
When used as directed, fluoride remains highly effective and is considered safe for most people. However, overexposure—especially in children—can lead to dental fluorosis, which is why understanding how fluoride toothpaste works and following proper usage is key.
Fluoride is often the first line of defense against decay and remains a staple in oral hygiene across the globe. But as patients explore alternatives like fluoride-free toothpaste, it’s important to consult with dental professionals to determine what’s best for your needs.
Key Differences in Chemical Properties and Bioactivity
Hydroxyapatite and fluoride both support enamel health, but they work through different mechanisms. The table below highlights their key differences to help guide your dental care choices.

Mechanisms of Action Across Applications
Knowing how hydroxyapatite and fluoride work is key to understanding their roles in dental and medical applications. While both compounds aim to strengthen and protect tooth enamel, they do so through different processes that reflect their unique chemical properties.
How Hydroxyapatite Works
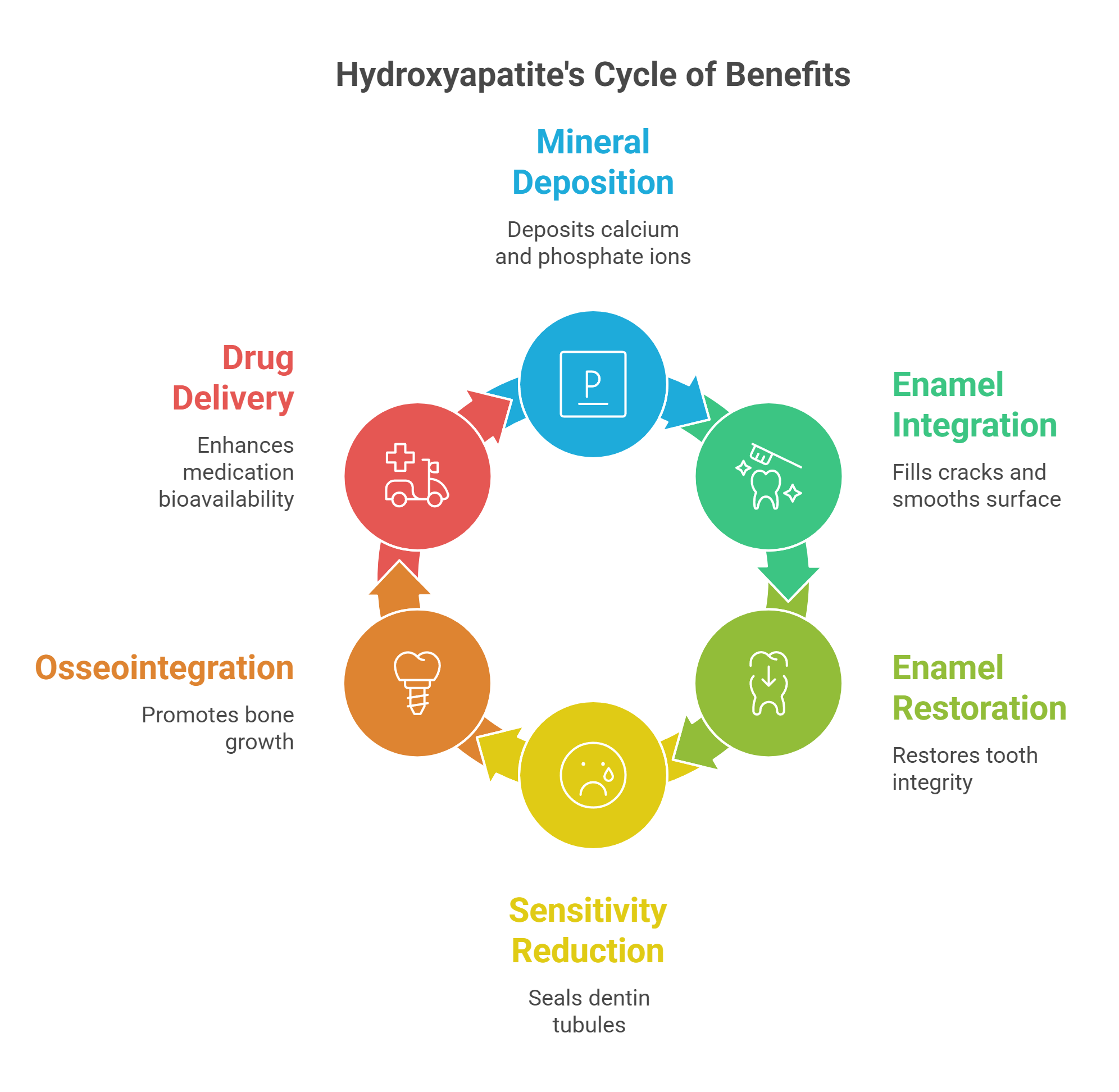
Hydroxyapatite works by:
-
Depositing calcium and phosphate ions onto the tooth surface effectively replenishes lost minerals and promotes enamel remineralization.
-
Integrating into the enamel structure, filling cracks, and creating a smoother, more resilient surface.
-
Restoring the integrity of the tooth enamel.
-
Helping reduce tooth sensitivity by sealing exposed dentin tubules.
In medical applications, hydroxyapatite’s biocompatibility and ability to promote osseointegration make it invaluable for bone grafts and implants. It acts as a carrier for therapeutic agents in drug delivery systems, improving medication bioavailability and reducing systemic side effects. These varied applications underscore hydroxyapatite’s versatility and effectiveness across different fields.
How Fluoride Works
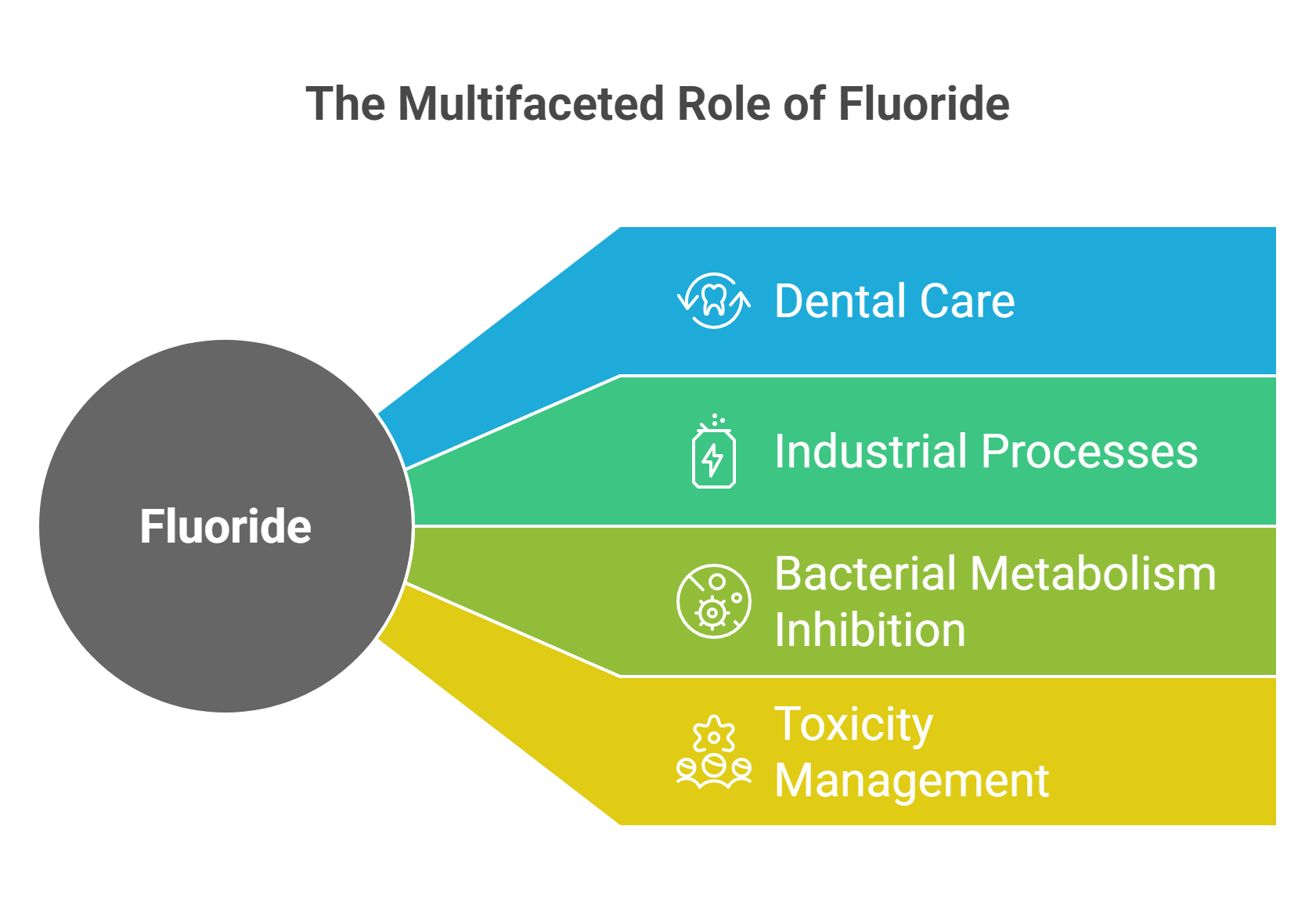
Fluoride’s primary function in dental care includes:
-
Promoting the formation of fluorapatite, a compound more resistant to acid attacks than hydroxyapatite.
-
Creating a protective layer on the tooth surface that reduces the solubility of enamel.
-
Inhibiting the action of acids produced by bacteria.
-
Helping in the remineralization of weakened enamel.
-
Protecting against cavities.
Beyond its dental applications, fluoride also plays a role in industrial processes, such as aluminum production and chemical processing. Its ability to inhibit bacterial metabolism through enzymatic mechanisms further underscores its utility in maintaining oral health.
While effective, managing fluoride exposure is important to avoid potential toxicity.
Clinical Efficacy and Research Evidence
Research consistently shows the effectiveness of both hydroxyapatite and fluoride in preventing dental caries and promoting oral health. Research evidence supporting their use highlights their proven benefits and applications.
Clinical Studies on Hydroxyapatite Applications
Studies indicate the following about hydroxyapatite toothpaste:
-
It can remineralize enamel as effectively as fluoride toothpaste.
-
A year-long trial demonstrated that hydroxyapatite was not inferior to fluoride control in preventing dental caries.
-
It has been shown to significantly reduce tooth sensitivity and sensitive teeth by sealing exposed dentin tubules. Additionally, understanding how hydroxyapatite toothpaste works can further enhance its benefits.
Beyond dental applications, hydroxyapatite has demonstrated anti-tumor effects, accelerated wound healing properties, and successful outcomes in orthopedic surgeries and bone grafts. These findings underscore hydroxyapatite’s versatility and effectiveness across various medical fields.
Clinical Studies on Fluoride Applications
Fluoride’s effectiveness in preventing cavities and dental caries is well-documented, with numerous studies confirming its benefits.
The American Dental Association endorses fluoride as the primary method for cavity prevention, citing its long-term safety and effectiveness. Community water fluoridation, for instance, has been shown to reduce tooth decay by at least 25% across populations, especially in discussions of fluoride vs other methods.
Epidemiological studies support fluoride’s role in reducing dental decay rates, particularly in areas with fluoridated water supplies. Fluoride toothpaste formulations have consistently demonstrated significant decreases in tooth decay, further solidifying its status as a cornerstone of modern dental care to prevent tooth decay. Understanding how fluoride toothpaste works is essential for effective oral hygiene.
Comparative Effectiveness Analysis
When it comes to strengthening enamel and preventing cavities, both hydroxyapatite and fluoride have proven to be highly effective. Numerous clinical studies suggest that their performance in enamel remineralization and cavity prevention is comparable, with no major differences in overall outcomes for most users.
However, emerging research points to a promising approach: using hydroxyapatite and fluoride in sequence rather than choosing between them. This combination may offer a synergistic effect, enhancing the enamel’s resistance to acid attacks and improving the overall remineralization process. As interest in integrative dental care grows, this dual-strategy approach could shape the next generation of preventive dental treatments.
Safety Profiles and Risk Assessment
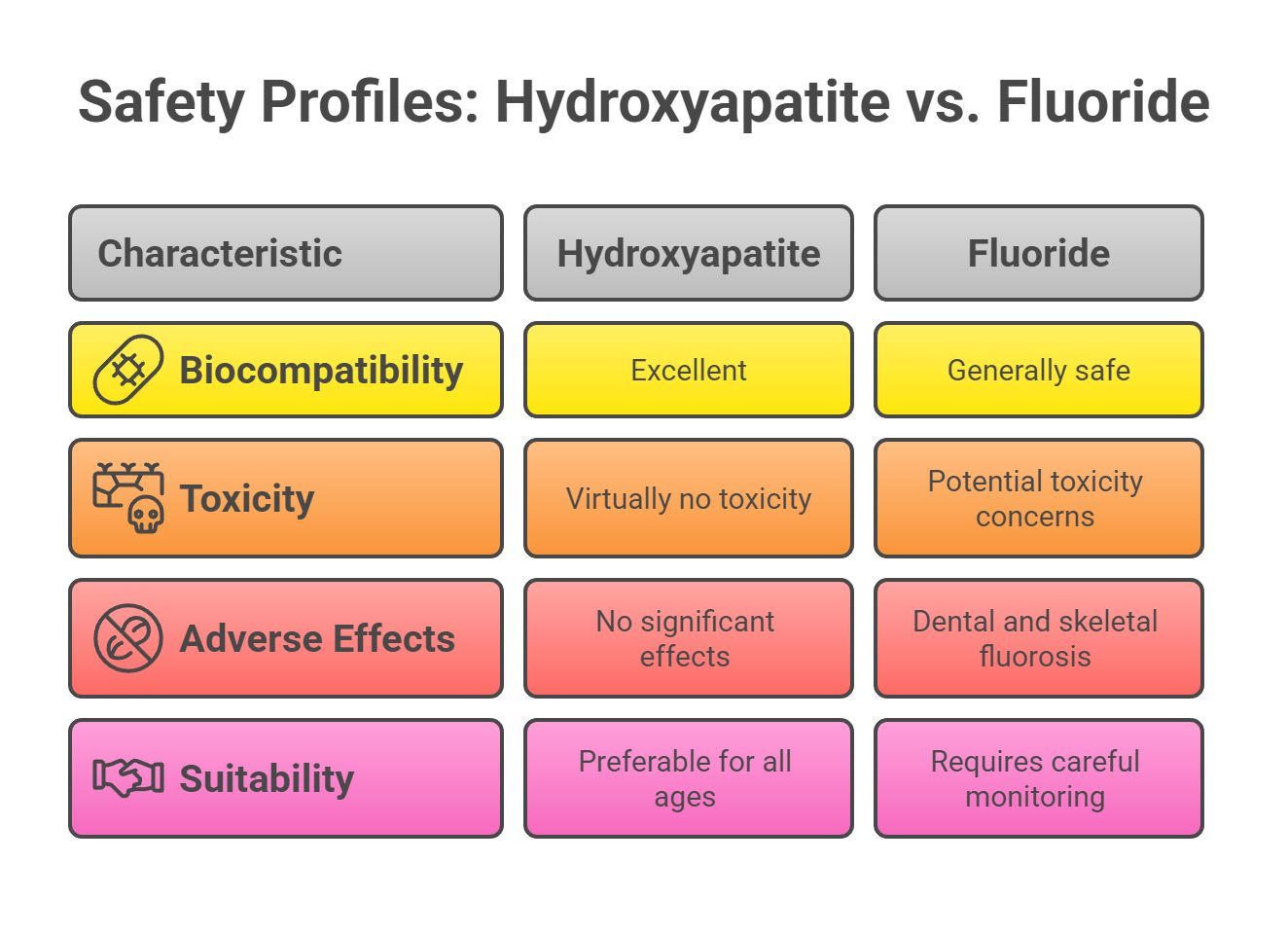
Safety is a paramount concern when evaluating dental and medical treatments. This section delves into the safety profiles of hydroxyapatite and fluoride, assessing their risks and benefits.
Safety of Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite is known for its excellent biocompatibility, making it suitable for a wide range of dental and medical applications. Unlike fluoride, hydroxyapatite presents virtually no toxicity concerns and is safe enough to swallow, making it a non-toxic alternative for daily use. Its natural origin and seamless integration into biological systems without adverse immune responses further highlight its safety.
Long-term studies have confirmed hydroxyapatite’s safety in implants and other medical applications, with no significant adverse effects reported. This makes hydroxyapatite a preferable choice for patients of all ages, including children, who are more susceptible to the potential risks of fluoride.
Safety of Fluoride
Fluoride is generally safe and effective when used in recommended amounts, with guidelines from organizations like the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry ensuring its safe use. However, excessive fluoride exposure can lead to dental fluorosis, skeletal fluorosis, and other toxicity concerns such as nausea and vomiting.
Following recommended guidelines on fluoride intake can minimize these risks, especially for vulnerable groups like young children. Proper education and monitoring are essential to ensure the safe use of fluoride in both dental and public health applications.
Applications Beyond Dental Care
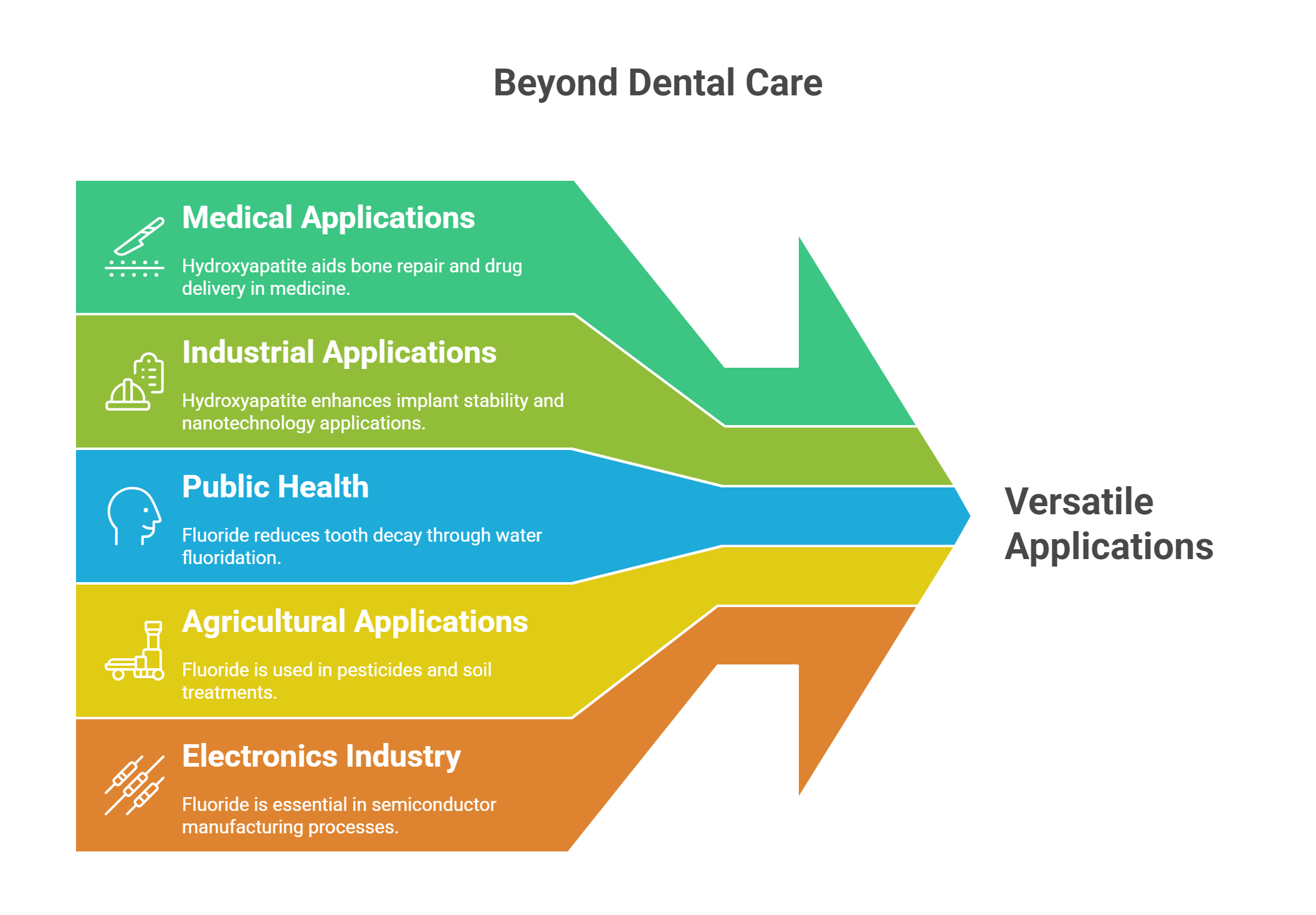
While hydroxyapatite and fluoride are primarily known for their dental applications, their uses extend far beyond oral health.
Hydroxyapatite in Medical and Industrial Applications
Hydroxyapatite is widely used in orthopedic and maxillofacial surgeries to aid in bone defect repair and promote regeneration. Its natural mineral structure allows it to mimic natural bone, making it an ideal material for bone grafting and implants. Additionally, hydroxyapatite serves as a carrier in drug delivery systems, improving targeted delivery and minimizing systemic side effects.
In industrial applications, hydroxyapatite coatings enhance the osseointegration of implants, leading to better stability and longevity. Advances in nanotechnology have further expanded its applications, with nano-hydroxyapatite offering enhanced surface area for improved biological interactions. This cutting-edge biomaterial science underscores hydroxyapatite’s versatility and potential in various fields.
Fluoride in Public Health and Industrial Applications
Fluoride’s most significant non-dental application involves community drinking water fluoridation, a public health intervention that has significantly lowered the incidence of dental cavities across various age groups since its introduction in 1945. The American Dental Association recommends maintaining a fluoride concentration of 0.7 milligrams per liter of water to optimize dental health benefits while minimizing risks. This practice has been associated with a 25% reduction in tooth decay across populations.
Beyond public health, fluoride is utilized in several industrial applications, including aluminum production, glass manufacturing, and chemical processing. It also plays a role in the agricultural sector, where it is used in pesticides and soil treatments.
The electronics industry benefits from fluoride’s properties in semiconductor manufacturing, showcasing its versatility and wide-ranging applications beyond dental care.
Economic Considerations and Market Accessibility
Economic considerations and market accessibility are crucial factors when comparing hydroxyapatite and fluoride products. Understanding the cost and availability of these compounds can help consumers and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Cost Analysis Across Applications
Hydroxyapatite products typically cost more than fluoride alternatives across dental and medical applications. The complexity of producing synthetic hydroxyapatite and formulating nano-hydroxyapatite contributes to these higher costs. For instance, hydroxyapatite-based toothpastes can be twice as expensive as fluoride toothpastes due to the advanced technology involved in their production.
In medical applications, the cost of hydroxyapatite implants and other treatments can also be higher, although insurance coverage and long-term benefits often justify the expense. Despite the higher initial costs, the effectiveness and safety of hydroxyapatite products make them a valuable investment in dental and medical care.
Market Availability and Accessibility
Fluoride-containing products benefit from established supply chains and regulatory approval processes, making them widely available at various price points. This accessibility ensures that fluoride products are suitable for different income levels and are readily available in both developed and developing countries. The extensive market penetration of fluoride products is due to their long history of use and proven effectiveness in dental care.
In contrast, hydroxyapatite products, particularly those containing nano-hydroxyapatite, are less accessible in many regions due to higher costs and less established distribution networks. Developing countries may face challenges in accessing these advanced dental products, highlighting the need for efforts to improve market availability and reduce costs.
Regulatory approval timelines and market entry barriers also play a role in the accessibility of hydroxyapatite products globally.
Professional Recommendations and Guidelines
Professional recommendations and guidelines are essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of hydroxyapatite and fluoride products.
This section explores the perspectives of dental and medical professionals and the regulatory frameworks governing these compounds.
Dental and Medical Professional Perspectives
Choosing between hydroxyapatite and fluoride often depends on individual needs and specific applications. Dental professionals advise consulting healthcare providers before changing dental care products or treatments to ensure optimal outcomes. Factors such as personal preference, specific medical needs, and treatment objectives influence the choice between hydroxyapatite and fluoride.
Professional societies and clinical guidelines are pivotal in guiding the use of these compounds. Dental professionals evaluate treatment efficacy based on individual patient circumstances, and their recommendations are informed by ongoing clinical studies and research evidence.
The primary goal remains maintaining healthy teeth and overall oral health, whether using hydroxyapatite or fluoride.
Regulatory Status and Approvals
The regulatory status and approvals for hydroxyapatite and fluoride products involve thorough evaluation by agencies such as the FDA. These regulatory bodies ensure that products meet specific quality control standards and are safe for consumer use. International efforts aim to harmonize guidelines for dental products, promoting consistent standards globally.
Manufacturers must adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure the safety and effectiveness of hydroxyapatite and fluoride products. This regulatory oversight helps maintain consumer confidence and supports the widespread adoption of these compounds in dental and medical care.
Future Directions and Emerging Research
The future of dental and medical care will likely see continued advancements in the use of hydroxyapatite and fluoride. Emerging research and innovative applications hold promise for enhancing the effectiveness and safety of these compounds.
Innovative Applications and Research Frontiers
Combination therapies using both hydroxyapatite and fluoride are being explored to enhance oral health outcomes. These innovative approaches leverage the strengths of both compounds, offering a synergistic effect that could provide superior protection against tooth decay. Advances in nanotechnology are paving the way for improved delivery systems of hydroxyapatite, enhancing its bioactivity in dental applications.
Research is also focusing on personalized medicine approaches that tailor hydroxyapatite treatments based on an individual’s specific risk profile for dental issues. Sustainable production methods are being developed to reduce the environmental impact of hydroxyapatite applications, aligning with global efforts to promote eco-friendly practices.
These research frontiers highlight the potential for hydroxyapatite to revolutionize dental and medical care.
Final Thoughts
In summary, both hydroxyapatite and fluoride offer significant benefits for dental and medical applications. While hydroxyapatite excels in biocompatibility and safety, fluoride remains a cornerstone of cavity prevention. Understanding their distinct properties and applications allows for informed decisions that can lead to healthier teeth and overall well-being. As research continues to evolve, the future holds promising advancements that could further enhance the effectiveness of these compounds in promoting oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recommended amount of fluoride in drinking water?
The optimal recommended amount of fluoride in drinking water is 0.7 milligrams per liter, or 0.7 ppm, as advised by the American Dental Association. This level helps maintain dental health while minimizing risks.
Can hydroxyapatite toothpaste prevent tooth decay?
Hydroxyapatite toothpaste can indeed prevent tooth decay by inhibiting plaque-forming bacteria and promoting the remineralization of early caries lesions. This makes it an effective option for maintaining dental health.
What are the benefits of fluoride toothpaste?
Fluoride toothpaste effectively strengthens tooth enamel and prevents cavities by inhibiting plaque-causing bacteria. Using it promises better oral health and protection against decay.
Is hydroxyapatite toothpaste safe to use?
Hydroxyapatite toothpaste is safe to use and may even present fewer safety concerns than fluoride toothpaste. It is a beneficial alternative for dental care.
Can you use both nano-hydroxyapatite and fluoride?
Yes, you can use both nano-hydroxyapatite and fluoride, but be mindful of their concentrations and application methods as their effects may differ.



































































