Amoxicillin for tooth infection is a widely used antibiotic that effectively treats such conditions. It works by eliminating the bacteria causing the infection, reducing pain and swelling. Amoxicillin is often among the first line treatments and is the first-line antibiotic for a tooth infection in people who are not allergic to penicillin. In this article, we will cover its effectiveness, dosage, potential side effects, and other critical information you should know.
Key Takeaways
-
Amoxicillin is the gold standard antibiotic for treating tooth infections due to its broad-spectrum effectiveness against various bacteria, often resolving infections within 24-72 hours.
-
Proper use of amoxicillin is important for disease control and helps prevent antibiotic resistance, supporting effective treatment of bacterial infections.
-
Adhering to the prescribed dosage and administration guidelines is critical for maximizing amoxicillin’s effectiveness and preventing bacterial resistance.
-
Patients with penicillin allergies have alternative antibiotics available, such as azithromycin and clindamycin, ensuring safe and effective treatment options for tooth infections.
What Does Amoxicillin Do for a Tooth Infection?
Amoxicillin is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics for treating tooth infections. Belonging to the penicillin class, it works by disrupting bacterial cell wall formation, causing the bacteria to die off. This mechanism makes it highly effective against many of the bacteria responsible for dental infections. In fact, amoxicillin is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic in the world for dental infections, underscoring its global importance in dental care.
Dentists often choose amoxicillin as a first-line treatment because it works well against both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria — the kinds typically found in tooth abscesses, periodontal infections, and pulp-related infections.
A dental abscess, for example, forms when bacteria enter the pulp of a decayed or damaged tooth. If left untreated, the infection can spread through the root and into surrounding tissues — even into the bloodstream in severe cases. Amoxicillin helps stop the infection early, reducing pain, swelling, and risk of serious complications. However, not all tooth infections present with obvious symptoms; a silent tooth infection may not show typical signs but still requires treatment to prevent further complications.
It’s also a go-to choice because it tends to be well-tolerated, with fewer gastrointestinal side effects than some other antibiotics. Research shows that amoxicillin can start resolving dental infections in as little as 24 to 72 hours, making it both a fast and reliable option for patients in pain.
How Much Amoxicillin Should You Take for a Tooth Infection?
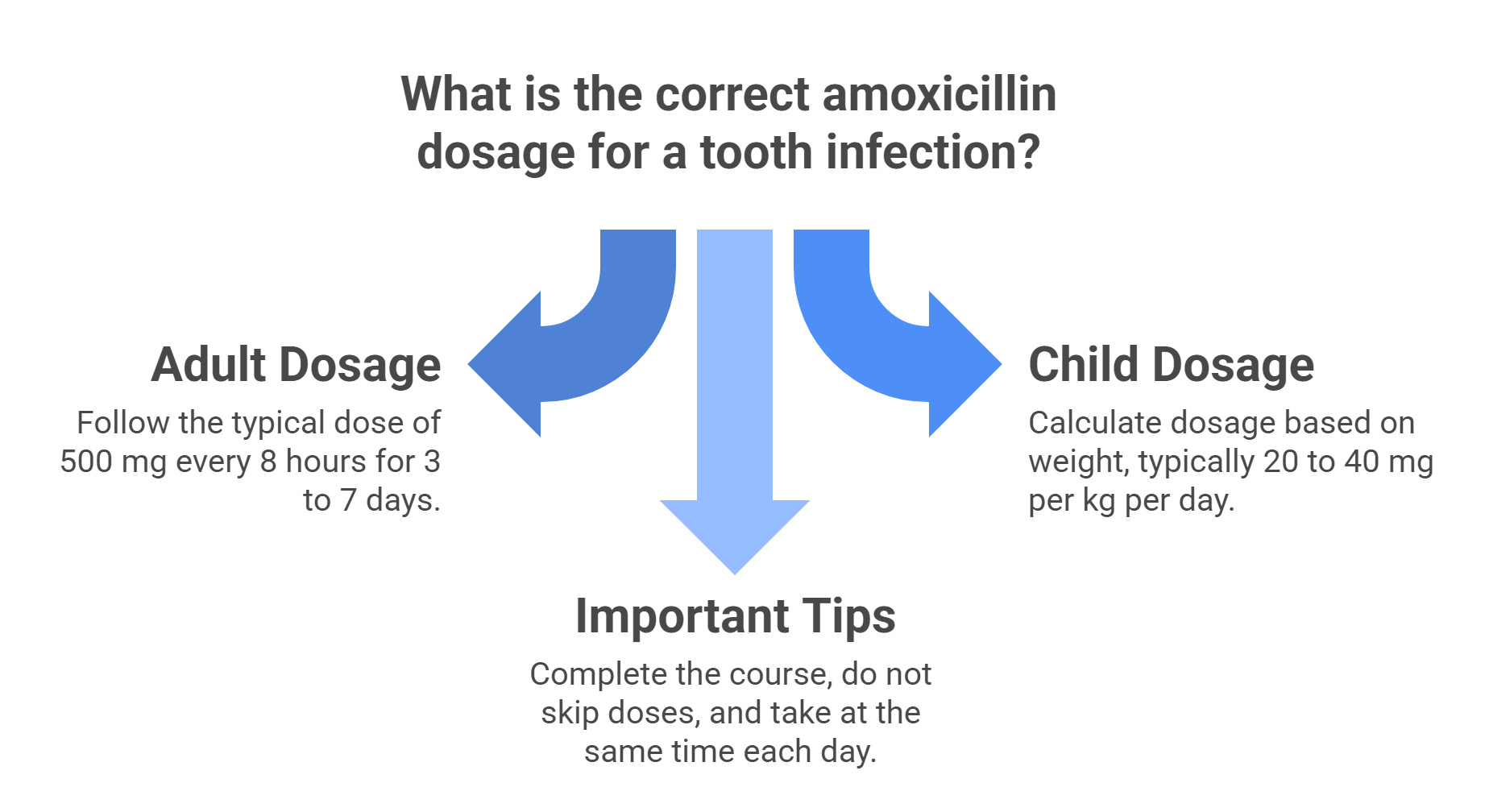
Getting the dosage right is essential when using amoxicillin to treat a tooth infection. Here’s a breakdown of common dosing guidelines — but always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
For Adults
-
Typical dose: 500 mg
-
How often: Every 8 hours (3 times a day)
-
Duration: 3 to 7 days, depending on the severity of the infection
For Children
-
Dosage is based on weight
-
Common range: 20 to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day
-
Usually divided into 2 or 3 doses throughout the day
Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food, but it should always be taken with a full glass of water and at evenly spaced intervals. This helps keep antibiotic levels consistent in your system.
Important Tips
-
Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication
-
Do not skip doses, as this can lead to bacterial resistance or recurrence
-
Take it at the same time each day for best results
Following these guidelines helps ensure amoxicillin works effectively to clear the infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Safety Profile and Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
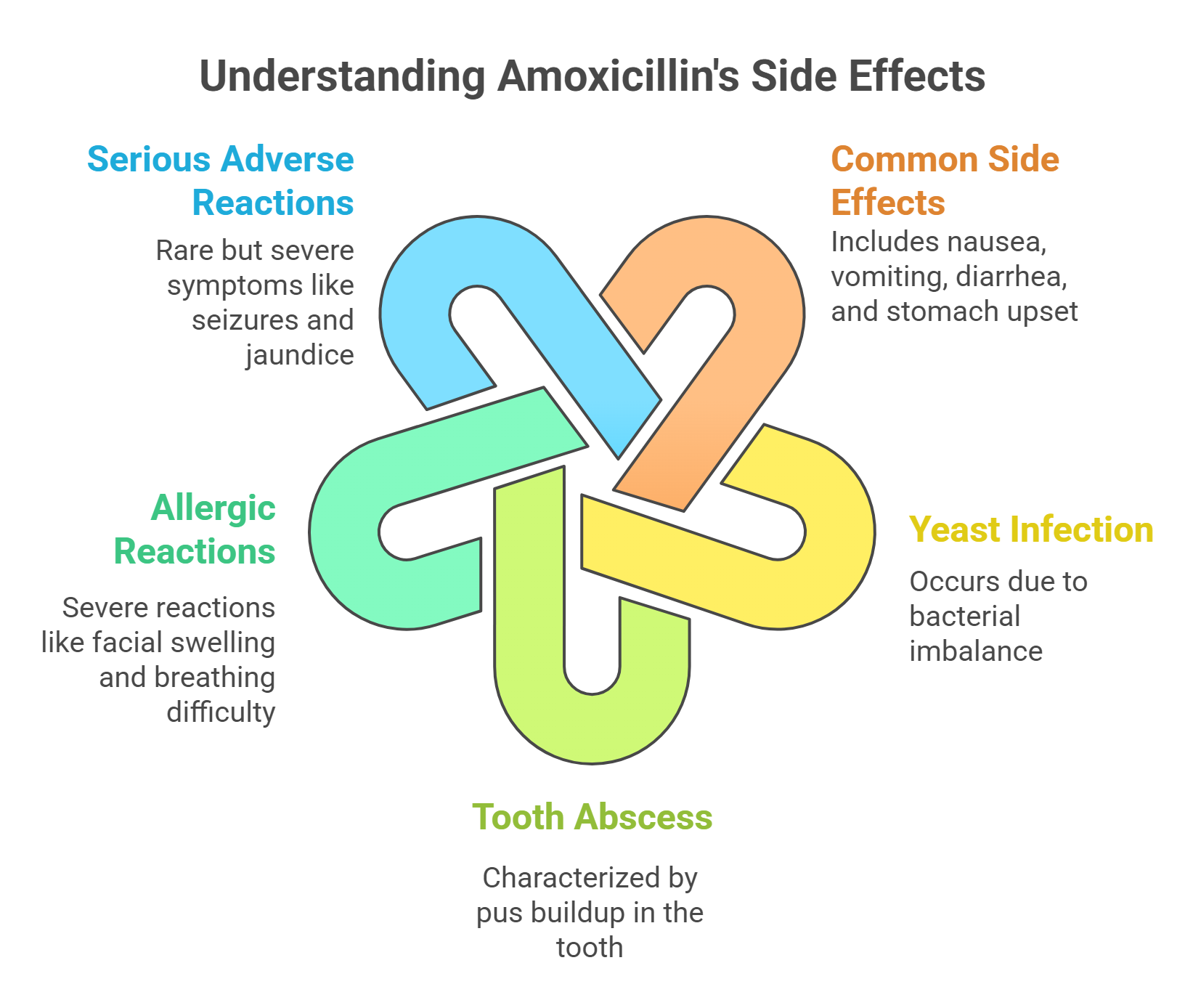
Like all medications, amoxicillin comes with its own set of potential side effects. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal in nature, including symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset. In some patients, amoxicillin may lead to a yeast infection due to disruption of the normal balance of bacteria. Tooth abscesses can cause pus to build up in the sensitive area of the tooth.
-
nausea
-
vomiting
-
diarrhea
-
stomach upset
These side effects are relatively common, affecting more than 1% of patients.
In rare cases, patients may experience serious allergic reactions to amoxicillin. Signs of a severe allergic reaction include swelling of the face or throat and trouble breathing, which require immediate medical attention. Patients should be aware of these potential reactions, particularly if they have a known penicillin allergy.
Additionally, some patients might experience serious adverse reactions, though these are rare. Such reactions may include:
-
prolonged vomiting
-
extreme tiredness
-
seizures
-
severe stomach pain
-
jaundice
These symptoms necessitate immediate medical attention to prevent further complications.
Overall, while amoxicillin is generally safe and well-tolerated, being informed about its potential side effects is crucial for patient safety.
Factors That Affect How Long It Takes Amoxicillin to Work for a Tooth Infection
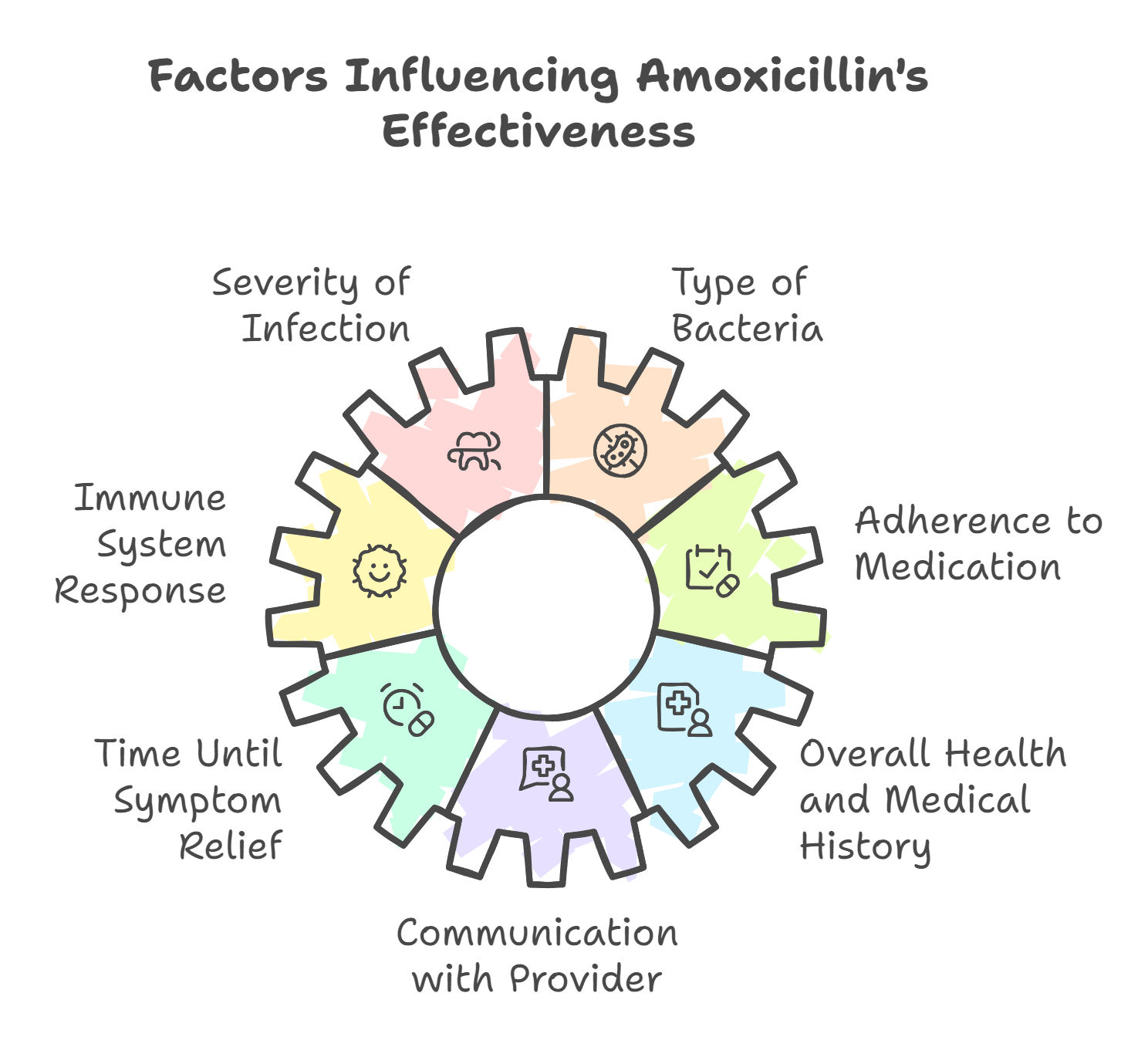
The recovery timeline for a tooth infection can vary based on several individual and clinical factors. Here's what influences how quickly you’ll feel better — and how long treatment may take:
-
Severity of the infection: More advanced infections may take longer to resolve and may require a longer antibiotic course or additional dental treatment.
-
Type of bacteria involved: Some infections involve more resistant strains or multiple types of bacteria (aerobic and anaerobic), which can affect treatment length.
-
Immune system response: Patients with strong immune systems typically recover faster, while immunocompromised individuals may need longer treatment.
-
Adherence to medication: Taking antibiotics exactly as prescribed is critical. Skipping doses or stopping early can lead to treatment failure or reinfection.
-
Time until symptom relief: Most people feel relief from pain and swelling within 24–48 hours. Significant improvement is typically seen within 72 hours.
-
Overall health and medical history: Pre-existing conditions may delay recovery and influence how your body responds to antibiotics.
-
Communication with your provider: Ongoing monitoring and reporting any unusual symptoms (or lack of improvement) to your dentist or doctor ensures timely adjustments to treatment.
Even if you feel better quickly, always finish the full course of antibiotics to prevent the infection from returning or spreading.
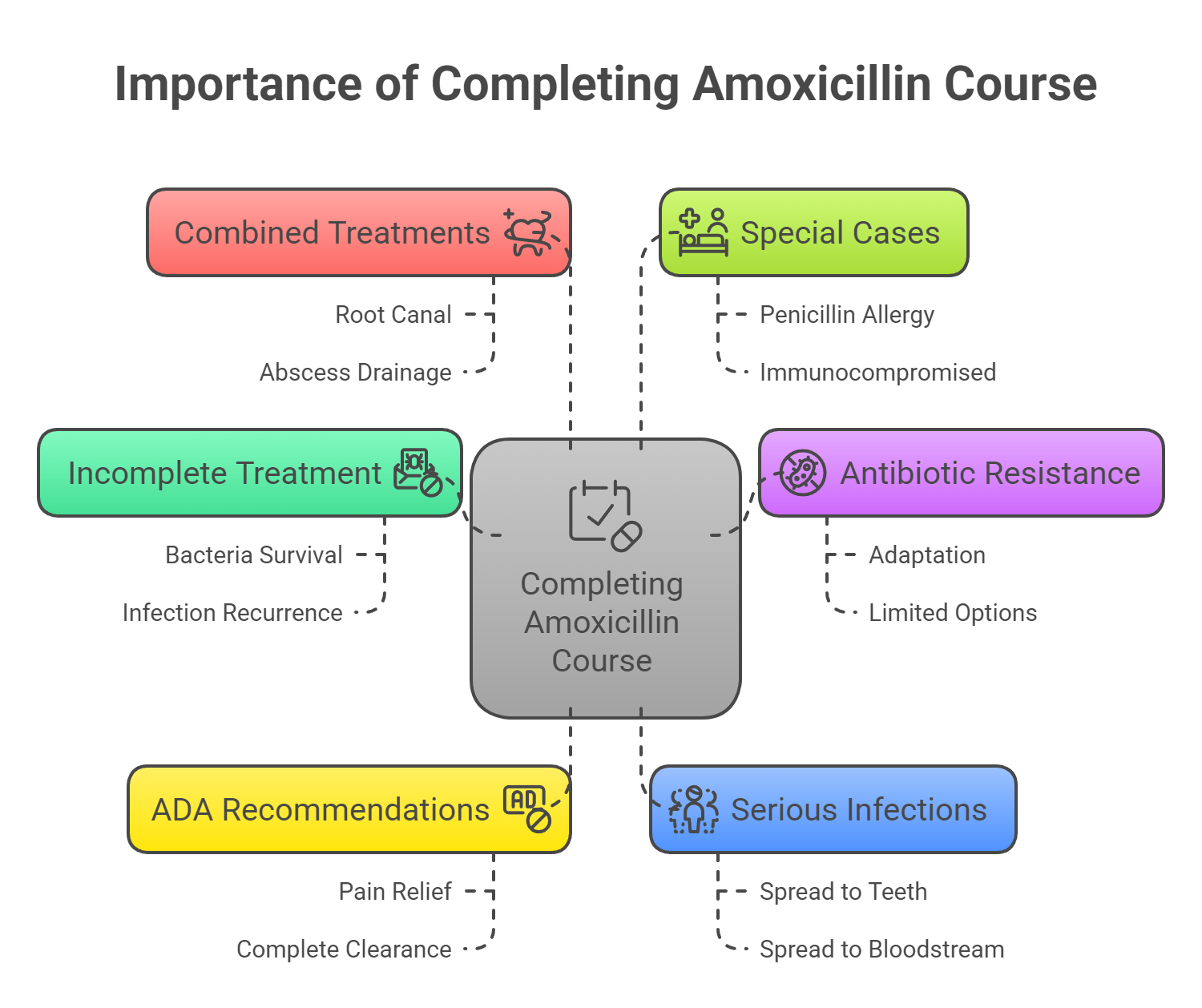
Why You Must Finish Your Full Course of Amoxicillin for a Tooth Infection
Taking amoxicillin exactly as prescribed is one of the most important steps in treating a dental infection effectively. Even if your pain or swelling improves within a couple of days, stopping the antibiotic too soon can lead to complications.
1. Incomplete Treatment Can Allow Bacteria to Return
If you stop taking amoxicillin early, some bacteria may survive. These remaining bacteria can begin to multiply again, causing the infection to come back — sometimes more severely than before.
2. Stopping Early Increases Antibiotic Resistance
When antibiotics are not taken as prescribed, bacteria can adapt and become resistant. This makes future infections harder to treat and limits your options for antibiotics that will still work.
3. The ADA Recommends Completing Every Prescription
The American Dental Association advises patients to always finish their prescribed antibiotics, even if symptoms have improved. Pain relief does not mean the infection is gone — only a full course can ensure complete bacterial clearance.
4. Serious Infections Can Spread
Untreated or partially treated dental infections can spread to nearby teeth, gums, bone, or even into the bloodstream. This is especially dangerous for patients with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
5. Amoxicillin May Be Combined with Other Treatments
In some cases, antibiotics alone aren't enough. Your dentist may also recommend a procedure like a root canal or abscess drainage. Finishing your antibiotics helps support these treatments and reduces the risk of reinfection.
6. Special Cases May Require Adjusted Care
Patients allergic to penicillin or those who are immunocompromised may need different antibiotics or closer monitoring. Always follow your provider’s guidance based on your medical history.
Final Reminder
Always take amoxicillin for the entire prescribed duration, even if you feel better. Doing so helps eliminate the infection fully, prevents it from spreading, and reduces the risk of future antibiotic resistance — protecting both your oral and overall health.
Contraindications and Alternatives for Patients with Penicillin Allergies
For patients who are allergic to penicillin, including amoxicillin, alternative antibiotics are available. Severe penicillin allergies often necessitate the use of other antibiotics such as azithromycin or clindamycin. These alternatives are effective in treating dental infections and are commonly prescribed when penicillin cannot be used.
Cephalexin is another alternative, but it requires caution for patients with penicillin allergies due to the potential for cross-reactivity. When selecting an appropriate antibiotic, healthcare providers consider the patient’s medical history and the type of bacteria involved in the infection. This tailored approach helps ensure that the chosen antibiotic is both safe and effective for the patient.
In some cases, metronidazole may be prescribed, particularly for anaerobic bacterial infections or as part of combination therapy with other antibiotics. Understanding these alternatives allows patients and healthcare providers to find the best treatment option for safely managing tooth infections.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Amoxicillin Use for Tooth Infections
Clinical evidence strongly supports the use of amoxicillin in treating tooth infections. Studies have shown that amoxicillin is highly effective in managing acute odontogenic infections, with clinical success rates ranging from 88-89%. Amoxicillin is preferred over penicillin for tooth infections due to its effectiveness against certain bacteria. This high success rate underscores the antibiotic’s reliability in resolving dental infections.
Systematic reviews have compared the effectiveness of amoxicillin with other antibiotics, such as amoxicillin/clavulanic acid and clindamycin. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has shown a clinical success rate of 88.2%, comparable to clindamycin’s 89.7%. These findings highlight amoxicillin’s efficacy and its comparable performance to other commonly used antibiotics.
Early antibiotic intervention with amoxicillin as a first line antibiotic is crucial for enhancing treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of complications. By starting treatment promptly, patients can achieve faster pain relief and prevent the spread of infection, making amoxicillin a cornerstone in dental infection management.
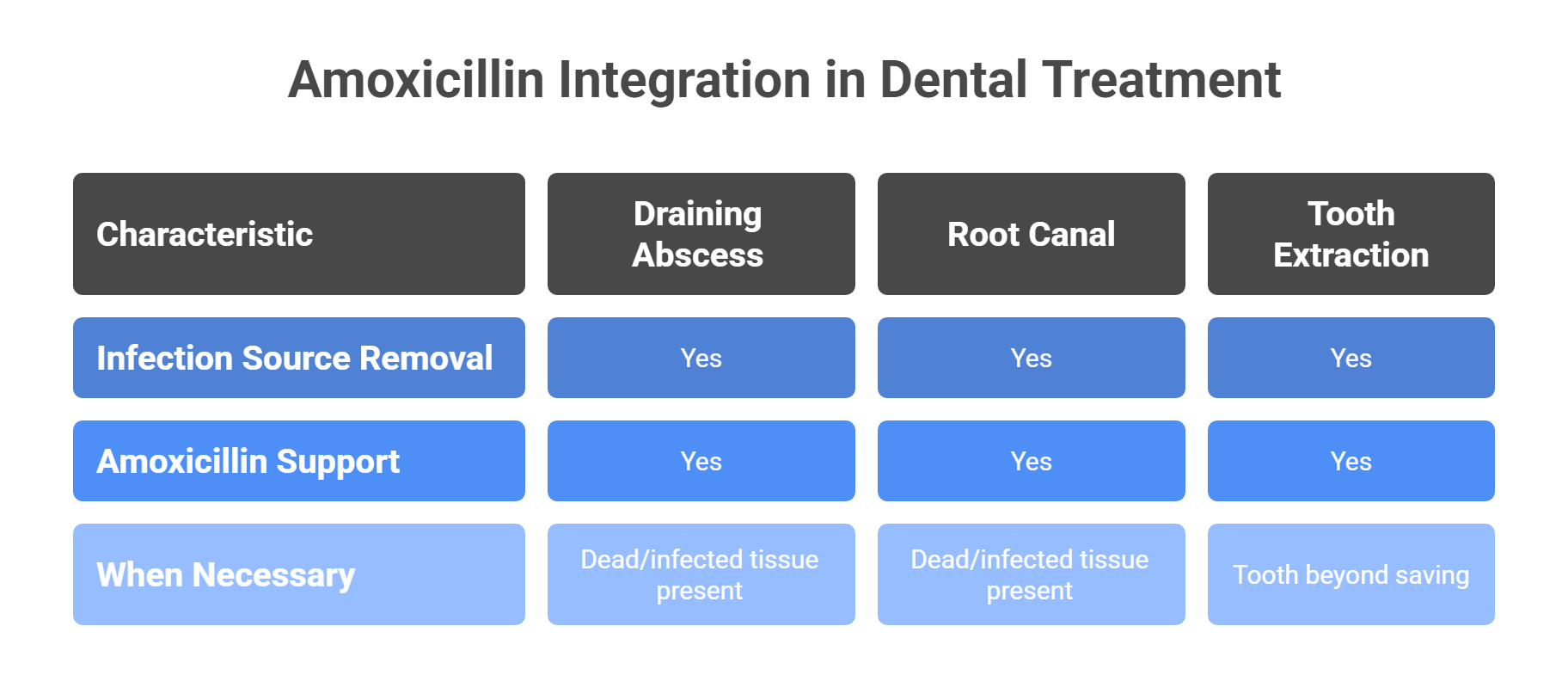
Integrating Amoxicillin into Dental Treatment Plans
While amoxicillin is highly effective at reducing bacterial infection, it’s rarely a standalone treatment for dental abscesses or severe tooth infections. To fully resolve the problem, antibiotics must be combined with proper dental procedures that address the source of the infection.
When Procedures Are Necessary
For infections involving dead or infected tissue, antibiotics alone are not enough. Common procedures used in combination with amoxicillin include:
-
Draining an abscess: Releases trapped pus and reduces pressure and swelling
-
Root canal treatment: Removes infected pulp and nerves, seals the root canal to prevent reinfection and the spread of infection
-
Tooth extraction: Necessary when a tooth is beyond saving due to infection or decay
These treatments eliminate the local source of infection, while amoxicillin works systemically to clear bacteria and prevent further spread.
Antibiotics as a Supportive Therapy
Amoxicillin is often paired with metronidazole in more complex or severe cases to increase antibacterial coverage — especially when dealing with anaerobic bacteria. This combination is especially helpful for:
-
Infections that are spreading
-
Patients with weakened immune systems
-
Situations involving swelling, fever, or systemic symptoms
The use of amoxicillin and metronidazole together is a common and effective approach in managing dental infections, particularly when broader antibacterial action is needed.
-
Infections that are spreading
-
Patients with weakened immune systems
-
Situations involving swelling, fever, or systemic symptoms
However, antibiotics cannot remove necrotic (dead) tissue or clean out infected tooth pulp — which is why dental procedures remain the cornerstone of treatment.
Why Integration Matters
By combining amoxicillin with the right dental intervention, healthcare providers can:
-
Quickly reduce pain and swelling
-
Prevent infection from spreading
-
Support faster recovery
-
Address both the symptoms and the cause of the infection
This integrated approach leads to better outcomes and helps preserve long-term oral health.
Managing Pain During Tooth Infection Treatment
Managing dental pain effectively is a crucial part of treating tooth infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are often recommended by dentists to help manage discomfort. The American Dental Association suggests starting pain management treatment with NSAIDs, including:
-
Ibuprofen
-
Naproxen
-
Celecoxib
-
Aspirin These medications are effective in reducing both pain and inflammation.
Tooth infections can also cause pain and swelling in the surrounding soft tissue, which may require additional care during recovery.
For enhanced pain relief, consider the following options:
-
Acetaminophen can be used in conjunction with NSAIDs, although it does not have anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Topical anesthetics containing benzocaine can provide immediate numbness to the affected area, offering short-term relief from tooth pain.
-
Applying a cold compress can help numb pain and reduce inflammation.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is also important during treatment. Here are some helpful practices:
-
Brush twice daily
-
Floss regularly
-
Rinse with warm salt water to help alleviate discomfort and promote healing
-
Stick to soft foods to prevent further irritation and allow the affected area with gum tissue and swollen gums to heal more effectively, avoiding hard or crunchy foods.
Preventing Future Dental Infections
Preventing future dental infections requires a proactive approach to oral health, including:
-
Regular dental visits
-
Good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing
-
Using mouthwash, like chlorhexidine, to help treat dental infections and reduce bacterial growth, along with necessary dental work to prevent infections and gum disease.
Maintaining oral hygiene and regular dental visits can also help prevent periodontal diseases, which are a significant risk factor for tooth infections.
Amoxicillin helps eliminate harmful bacteria causing infections, maintaining a healthy oral microbiome and reducing the risk of complications. However, it is crucial to address the underlying causes of infections through regular dental evaluations. This can help prevent the recurrence of infections and ensure long-term oral health.
Professional cleanings and dental hygiene are vital in preventing tooth infections that require antibiotic treatment. By adhering to these preventive measures, patients can significantly reduce their risk of developing dental infections and the need for antibiotic therapy.
When to Seek Further Medical Attention
Preventing future dental infections requires a proactive approach, including regular dental visits, good oral hygiene, and addressing underlying causes through professional evaluations. An infected tooth should never be ignored; it requires prompt professional evaluation to prevent complications. A tooth infection should always be treated. By integrating amoxicillin into a comprehensive dental treatment plan and managing pain effectively, patients can achieve optimal oral health and prevent the recurrence of infections. Remember, prompt and appropriate treatment is key to overcoming tooth infections and maintaining a healthy smile.
Monitoring symptoms closely and being aware of when to seek further medical attention can prevent complications and ensure effective treatment options. If symptoms do not improve within one week or worsen during treatment, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately for an ongoing infection. If symptoms do not improve with initial treatment, a dentist may need to reassess and suggest different treatment options.
Prompt action can help address any issues that may arise and ensure immediate relief for a successful recovery.
Summary
Amoxicillin remains a trusted and effective treatment for tooth infections, especially when paired with proper dental care and completed as prescribed.
While it plays a vital role in stopping active infections, preventing them in the first place is just as important. Maintaining strong enamel and a healthy mouth through daily care can help you avoid infection and reduce your reliance on antibiotics.
If you're looking to support your oral health and prevent future issues, a high-quality toothpaste like SNOW’s hydroxyapatite formula offers daily protection — helping you keep your smile strong, clean, and cavity-free.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recommended dosage of amoxicillin for treating a tooth infection?
For adults, the recommended dosage of amoxicillin for a tooth infection is usually 500 mg taken three times a day for 3 to 7 days. In children, the dosage typically ranges from 20 to 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, divided into two or three doses.
What are common side effects of taking amoxicillin?
Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Although rare, serious allergic reactions can occur, presenting as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face or throat.
What should a patient do if symptoms do not improve after taking amoxicillin?
If symptoms do not improve after taking amoxicillin, it's crucial to contact your dentist for reassessment, especially if there is no improvement after three days. Seeking further medical attention may be necessary if symptoms worsen. If symptoms do not improve after completing amoxicillin, a dentist may recommend a different antibiotic such as metronidazole.
Are there alternatives to amoxicillin for patients with penicillin allergies?
Yes, patients with penicillin allergies can consider alternatives such as azithromycin, clindamycin, and metronidazole, though cephalexin should be used with caution due to potential cross-reactivity. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable option.
How can future dental infections be prevented?
To prevent future dental infections, maintain good oral hygiene by regularly brushing and flossing, using mouthwash, and attending dental check-ups for professional cleanings and evaluations. These practices are essential for addressing and managing any underlying issues effectively.